Let's start
Prerequisites
Before developing in Flutter, it's beneficial to have some prerequisites and a foundation in the following areas:
Dart Programming Language: Flutter uses the Dart programming language. While you can learn Dart alongside Flutter, having a basic understanding of Dart before starting with Flutter development will be advantageous.
Programming Fundamentals: Solid knowledge of programming fundamentals like variables, data types, control structures (if, for, while), and functions is essential.
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): Flutter and Dart are based on OOP principles. Understanding concepts like classes, objects, inheritance, and polymorphism is crucial.
Integrated Development Environment (IDE): You'll need an IDE for Flutter development. Android Studio with the Flutter plugin or Visual Studio Code with the Dart and Flutter extensions are popular choices.
User Interface (UI) Principles: An understanding of UI/UX design and layout concepts is valuable for creating user-friendly Flutter apps.
Command-Line Interface (CLI): Flutter development involves using the command line for various tasks like project creation, running the app, and managing dependencies. Familiarity with CLI basics is necessary.
APIs and Networking: If your app needs to interact with web services, having knowledge of API integration and networking concepts will be beneficial.
Asynchronous Programming: Flutter apps often require asynchronous tasks. Understanding async/await and futures is important.
Introduction
Mobile contraints
| OS (Operating System) | Mobile OS |
|---|---|
| Link hardware and software | Battery |
| HMI: Human-Machine Interface | Touch screen, virtual keyboard, screen size |
| Perform calculations, execute calculations, provide services | Sensors (gyroscope, NFC, light meter, GPS chip, GSM chip, …) |
| Enigma, punched card, terminal, command-line interface, graphical interface | (Power) <= no longer relevant, PCs now even have ARM chips |
| Ubiquity | |
| Security |
What is Flutter?
Flutter is a groundbreaking open-source UI framework developed by Google that allows developers to build high-quality, natively compiled applications for various platforms, including mobile, web, and desktop, using a single codebase. Flutter's primary advantage lies in its extensive library of customizable widgets, which enables developers to create stunning and highly performant user interfaces.
Flutter's History
Flutter had its inception within Google under a project known as "Sky." However, it was officially introduced as an open-source framework in May 2017, when Google announced its first stable version. Over the years, Flutter has undergone significant growth and evolution.
Here's a brief overview of some key Flutter versions:
Flutter 1.0 (December 2018): This marked the official release of Flutter, providing a stable foundation for app development. It introduced core features and widgets.
Flutter 1.12 (December 2019): This version introduced major improvements, such as support for Android App Bundles and continued to enhance the developer experience.
Flutter 2.0 (March 2021): A milestone release that introduced several significant enhancements, including web and desktop support. Flutter 2.0 empowered developers to target more platforms with a single codebase.
Here are the top 5 features of Flutter 3 (2022)
Full Support for International Text Input on Desktop Platforms: Flutter now offers comprehensive support for international text input, including languages with complex text input methods (IMEs), on all desktop platforms. This includes third-party IMEs like Sogou and Google Japanese Input.
Accessibility on All Desktop Platforms: Flutter for Windows, macOS, and Linux now supports accessibility services, making it more accessible to users with disabilities. This includes screen-readers, accessible navigation, and inverted colors.
Universal Binaries on macOS: Flutter macOS desktop apps are now built as universal binaries, ensuring native support for both Intel-based Macs and Apple Silicon devices.
Deprecating Windows 7/8 for Development: The recommended Windows version for Flutter development has been raised to Windows 10. While older versions like Windows 7 and 8 are not blocked, they are no longer officially supported, encouraging developers to upgrade.
Mobile Updates: Flutter 3 introduces several mobile updates, including support for foldable mobile devices, iOS variable refresh rate support for smoother animations, simplified iOS app releases, and a Gradle version update.
Changelogs
You can find the complete release notes and changelogs for each Flutter version at the official Flutter documentation
Flutter platforms support
| Platform | Version supported |
|---|---|
| Android | 24 to 36 |
| iOS | 13 to 26 |
| Chrome,Firefox,Safari | Latests |
| Windows | 10, 11 |
| macOS | Catalina (10.15) to Tahoe (26) |
| Linux | 20.04 LTS to 24.04 LTS |
Supported Platforms
You can find the complete list of supported platforms and their details at the official Flutter documentation
The Flutter Architecture
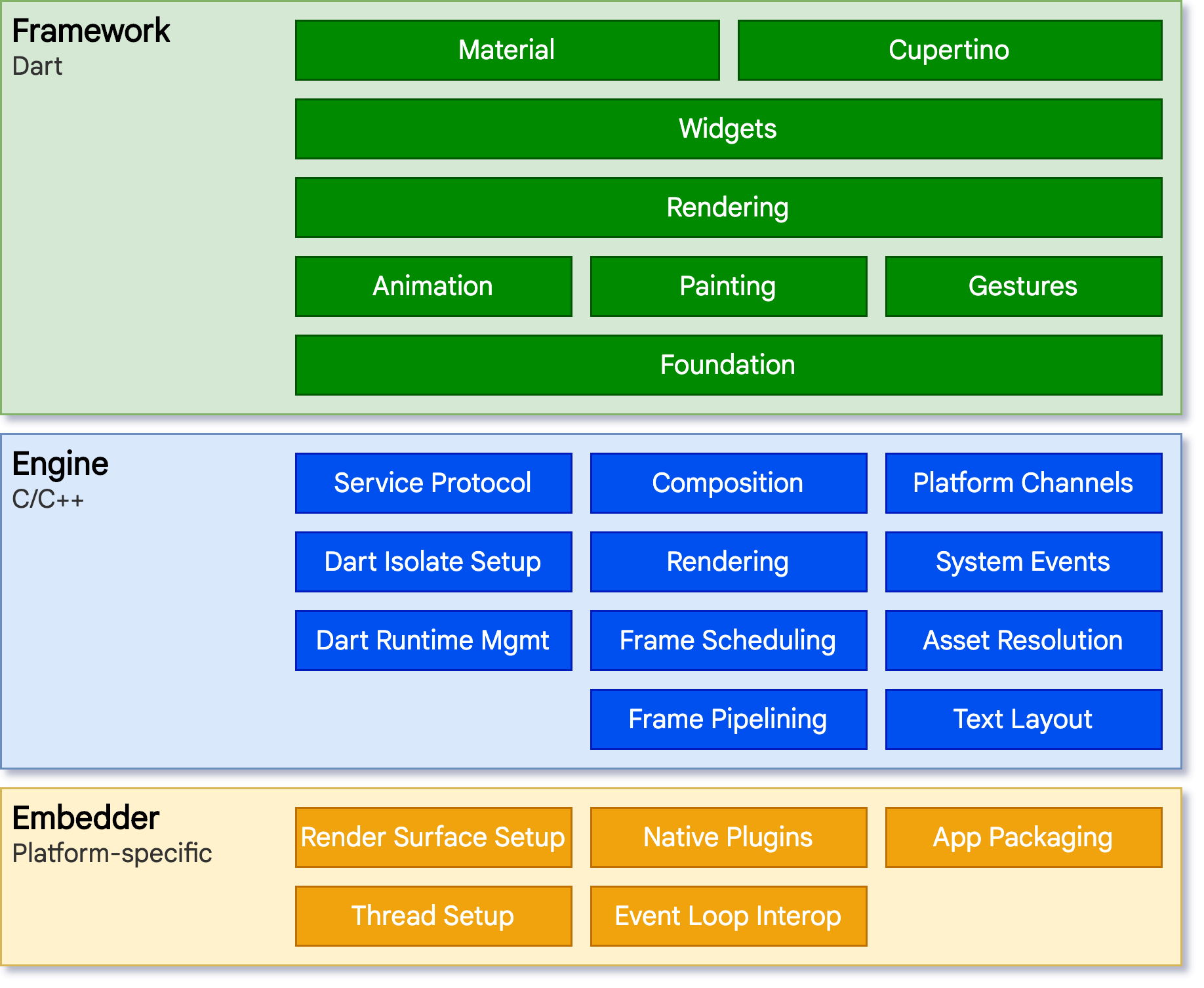
To understand how Flutter operates, it's essential to delve into its architecture. Flutter adheres to a layered architecture with the following components:
Framework Layer: This is where the core building blocks of Flutter reside. It provides a rich library of widgets for constructing user interfaces, manages gestures, animations, and layout, and is the foundation for app development.
Engine Layer: The engine handles the rendering of the user interface. It offers a low-level rendering framework that interfaces with the graphics hardware of the target platform. Additionally, it manages platform-specific services like sensors and cameras.
Embedder Layer: The embedder integrates Flutter into the specific platform, whether it's Android, iOS, web, or desktop. It facilitates communication between the Flutter engine and the host platform, ensuring seamless integration.
Flutter's architecture is designed to deliver exceptional performance and responsiveness, making it a top choice for a wide range of development projects.
